What is Generative AI?
 Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), powered by machine learning models, is a technology that produces new content in a range of formats. This type of AI, currently exemplified by tools like Open AI's ChatGPT and DALL-E, Microsoft's Copilot (formerly Bing AI), Google's Gemini (formerly Bard) and Midjourney, learns from vast amounts of training data (i.e., examples) and is able to generate content that is entirely novel.
Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI), powered by machine learning models, is a technology that produces new content in a range of formats. This type of AI, currently exemplified by tools like Open AI's ChatGPT and DALL-E, Microsoft's Copilot (formerly Bing AI), Google's Gemini (formerly Bard) and Midjourney, learns from vast amounts of training data (i.e., examples) and is able to generate content that is entirely novel.
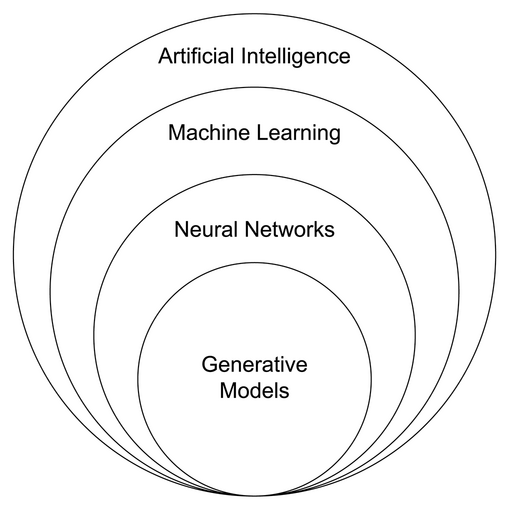
Machines programmed to learn from examples are known as neural networks. One type of neural network is the language model; "Large Language Models" (LLMs) like ChatGPT are trained on large volumes of text, resulting in an ability to "predict" what word should likely come next in a sequence of words. A generative model can draw upon what it has "learned" from training data and create something entirely new based on a complex synthesis of that information.
Though the quality and reliability of the output produced by these tools is evolving quickly, they are currently prone to generating unreliable information and errors at times. These include, for example, suggesting references for resources (e.g., books and articles) that do not exist.
The Original Benny C, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
| Generative AI | |
| Capabilities | Limitations |
|
In response to prompts (inputs), generative AI can ...
To learn more about generative AI capabilities, visit:
|
Misinformation and Disinformation
Privacy and Security
Legal and EthicaI Issues
To learn more about these and other issues associated with generative AI, visit:
|